April 5, 2021
Everyone in the world has to relieve themselves throughout the day. Your body is designed to process nutrients and create waste that you have to get rid of somehow. This is where your urinary tract comes in. Your bladder is responsible for getting urine and other fluids out of your body once the nutrients have been absorbed. When everything flows as normal, you can go to the bathroom without any issues. However, there are infections that can happen in this area of the body that can cause pain and discomfort or interfere with your urinary system.
A Urinary Tract Infection, or UTI, is an infection in any part of your urinary tract from the kidneys or ureters but most commonly with the bladder or urethra. Typically a UTI is an easily treatable medical condition that doesn’t get too threatening unless it spreads to the kidneys or beyond. Mainly it is just an annoyance or temporary discomfort that can be treated with antibiotics or at-home remedies. There are steps you can take to avoid getting a UTI by taking care of your general hygiene and monitoring your symptoms. Let’s look at some general information about UTIs, symptoms and causes, and when you may need to consult a healthcare provider.
Anatomy of your Urinary Tract
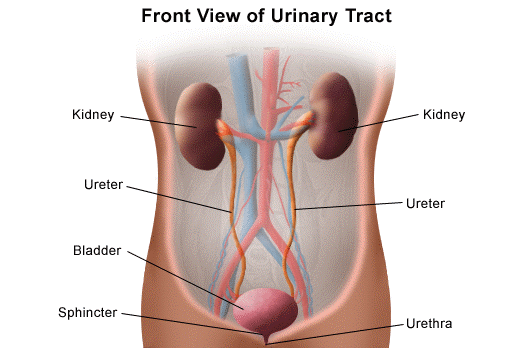
In order to understand how a UTI may happen, it helps to understand the anatomy of your urinary system. The main purpose of this system is to filter your bloodstream and produce urine to get waste out of the body. This involves your kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The kidneys start off the process of removing waste and balancing your body’s fluids. Urine then moves through your ureters to the bladder where it collects until it is time to relieve yourself. The urethra is the tube where your urine leaves the body. Depending on which part of your urinary tract is affected by your UTI, you may experience different symptoms and complications. Your body is a well-oiled machine, so one problem can cause irritation in multiple areas.
Symptoms
While each type of UTI will cause specific symptoms, there are some general ones to look out for. Everyone is different and some individuals may not even deal with UTI symptoms when they have the infection. Here are a few signs or common UTI symptoms that you may need to speak to a healthcare provider about your irritation:
- Continuous or frequent urination
- A burning sensation or painful urination
- Abnormal urine color, consistency, or smell
- Blood in your urine
- Abdominal pain
- Pelvic pain
- Chills or fever (in more serious infections)
If you start to notice any of these symptoms, there’s a good chance you should meet with your primary care provider or an urologist for medical advice. The best way to cure these side effects is to resolve the underlying infection.
Types of Urinary Tract Infection
As mentioned above, different types of UTIs will cause different issues. While this is a common infection, you do want to make sure it doesn’t spread or affect more serious organs. Let’s look at the different types of urinary tract infections so you can know what to prepare for.
Cystitis (Bladder)
If you are experiencing abdomen discomfort or pelvic pressure, that is a sign of a UTI in your bladder directly. This is known as cystitis and can result in painful urination or within your bowels.
Urethritis (Urethra)
Urethritis is exactly how it sounds. This type of UTI affects your urethra or genital area directly. This will usually only result in discharge or a burning sensation when you pee.
Pyelonephritis (Kidneys)
The UTI that can cause more serious complications or a potential medical emergency is pyelonephritis. This is an infection within your kidneys. This untreated UTI can often affect parts of the body beyond your urinary tract. You may experience fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, or intense back pain as a result of your kidneys working to regulate the body.
Causes of a UTI
A UTI happens when bacteria enters the urinary system and causes complications. The whole purpose of the urinary tract is to keep this kind of serious infection out, but sometimes your body’s defenses can’t protect against anything. Truthfully, your urethra is very close to the anus, so E. Coli and other waste products can sometimes get into the bladder that way. Luckily, there are simple ways to cure a UTI and good hygiene practices can help you reduce your risks.
Risks
While the cause of a UTI is simply bacteria getting into the urinary system, there are plenty of ways that can happen. Which puts you at risk for a serious infection called sepsis. Certain behaviors will put you at greater risk for this type of infection or a recurrence of the issues. Here are some risks to be aware of and ways you can work to prevent problems for yourself.
Women are at greater risk.
The female anatomy puts women at a higher risk of developing a UTI. Because the anus is so close to the urethra, it is more common for bacteria to travel between the two. A shorter urethra also means the infection doesn’t have to travel as far to get to your bladder. It is estimated that about half of all women will experience a UTI during their lifetime, sometimes dealing with recurrent urinary tract infections. While you can’t change your anatomy, it is a good idea to follow some other steps so you lower your risk of UTIs.
Intercourse
Sexual activity can increase your risk of UTIs, especially for women. This is why many people will advise you to urinate after sex or intercourse. A new sexual partner can introduce new types of bacteria into your system which is how the infection spreads. By taking care of your genital area after intercourse, you are protecting your vagina and urethra and helping your body stay healthy.
Birth Control
While oral contraceptives don’t increase your risk for UTIs, other forms of birth control may be a bad idea. Using condoms with spermicides or diaphragms introduce common bacterial infections and can leave you with different a urinary tract infection.
Menopause or Pregnancy
In general, women drew the short end of the stick when it comes to the risk of UTIs. Because of changes to hormones during menopause or pregnancy, these conditions can cause a bacterial infection in the urinary tract. Changes in estrogen can cause a bacterial shift in your vagina which can increase the risk of a UTI.
Wiping
When you were first learning to use the restroom as a child, the first rule your parents should have taught you is to wipe from front to back. Otherwise, you run the risk of bringing E. Coli bacteria from your anus into your urinary tract. Watching how you wipe is one of the best preventive measures you can take to avoid UTI complications.
Physical Abnormalities or Genetics
You may have an abnormality in your urinary system or with your genetic background that can increase your risk of a UTI. A blockage of the flow of urine out of your body can cause bacteria to build up which leads to that severe pain and discomfort.
Compromised Immune System
If you have a compromised immune system in the first place, you are already at risk for harmful bacteria entering your bloodstream. Be extra careful to monitor your other risks so that you don’t have to deal with a urinary tract infection on top of other issues.
Complications
While most lower urinary tract infections require a small amount of management to handle them quickly, there are times where this harmful bacteria can cause serious complications. If left untreated, you may experience recurrent UTIs within months of each other or for longer periods of time. When your urologic health is left unchecked, it can cause permanent damage to your kidneys which will affect your overall quality of life.
Finally, while any minor infection may seem like no big deal, there is potential for it to develop into sepsis. This is a life-threatening disorder that can cause inflammation throughout the body because your immune system is trying and failing to protect your bloodstream. Don’t let these severe symptoms threaten your health condition, instead get a UTI taken care of within a couple of days so you have that peace of mind.
When to See a Doctor
“A patient should come in and see their primary care provider for urinary tract symptoms if they have pain when they urinate, if they have any urgency or frequency, if they have blood in their urine, or if they’re having to race to the toilet. That’s a sign they should go see their primary care provider,” says Britney Cornett, PA-C.
If you are experiencing any symptoms of a UTI or problems with your urine flow, seek medical help. Your doctor will simply take a urine sample to see if there are active ingredients of harmful bacteria. They can then prescribe you antibiotics or offer other treatment options. If your medical history is full of mild UTI problems, it may be time to seek more advanced medical care to get to the bottom of your complications. A systematic review of your symptoms will help you find the proper treatment if it’s a more serious condition.
“Generally, if the patient will increase their fluid consumption that can help. But, if their symptoms linger, they should go in for an appointment so they can have a urine analysis and a urine culture done,” adds Cornett.
Treatment
When your doctor does recommend medical treatment, there are a few different courses they may take. Prescription medication will treat the infection and you should be back to feeling healthy in no time.
Antibiotics
Just like for any bacterial infection, antibiotics are the most common treatment option. Uncomplicated UTIs are often treated with first-line treatment: fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (in regions where the prevalence of Escherichia coli resistance does not exceed 20 percent). Beta-lactam antibiotics, amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefaclor, cefdinir, and cefpodoxime are not recommended for initial treatment because of concerns about resistance. Remember that the best treatment is to continue taking your antibiotics even if you start to feel better after a few days. Typically it shouldn’t take long for your symptoms to subside.
Fluids
As you’re working to rid your body of this bacteria, continue drinking a lot of fluids. Each glass of water will help flush that bad bacteria from your bladder and urinary tract. In addition to water, many people will try cranberry juice. While there is no official research to prove cranberries can reverse infection, the tannin in the berry can prevent E. Coli bacteria from sticking to your bladder wall. So if you’re looking for a simple, at-home remedy to try, grab beverages of unsweetened cranberry juice.
Heating Pad

Waiting for a UTI to pass can still involve back pain or abdominal pain. For these issues, try ibuprofen or heating pads as pain relievers. Even a hot water bottle on your pelvis or abdomen can help offer you some relief.
Prevention
Once you have been diagnosed with a UTI, there is nothing to do but treat the infection. However, there are plenty of ways to work to prevent the issue in the first place. The first step is to work on your hygiene and be aware of any risk factors you may have. Here are a few pieces of advice to aid your prevention of a UTI and the spread of bacteria.
Watch your wiping.
If wiping after using the restroom is a main cause of UTIs, it can be helpful to watch the way you wipe. Be sure you’re always going front to back and not mixing the opening of your urinary tract with your rectum or anus. This will stop the growth of bacteria before it even enters your system.
Drink your fluids.
A lot of water can help keep your body healthy in many ways. Drinking enough water works as disease control by flushing out unhealthy or bad bacteria. The more water you drink, the more often you’ll have to urinate as well, so the lining of the urinary tract will be less susceptible to severe infection.
Relieve yourself after sex.
Sexual intercourse can result in new bacteria being introduced into the urinary tract. The simple act of going to the bathroom first thing after sex will help keep bacteria out and take care of your health. This reduces the risk of kidney infection or bladder infection beyond your urinary tract.
Change up your feminine products.
For women, there are plenty of different products you may use for vaginal health. Avoid harmful dyes or irritating feminine products. Cornett emphasizes, “Avoid fragrance products in the vaginal area.” These can throw off the PH balance of your genital area which can increase your risk for UTIs. Let your body do its job to prevent infection and work to keep your urethra clean, unaffected, and healthy. “There’s some thought that cranberry tablets may help by acidifying the urine, they don’t treat a UTI but they can help with prevention,” says Cornett.
DISCLAIMER
The information featured in this site is general in nature. The site provides health information designed to complement your personal health management. It does not provide medical advice or health services and is not meant to replace professional advice or imply coverage of specific clinical services or products. The inclusion of links to other web sites does not imply any endorsement of the material on such websites.
